@aaronpk you linked to "Insufficient Redirect URI Validation" though? maybe i'm just confused about what you were talking about.
-
-
-
-
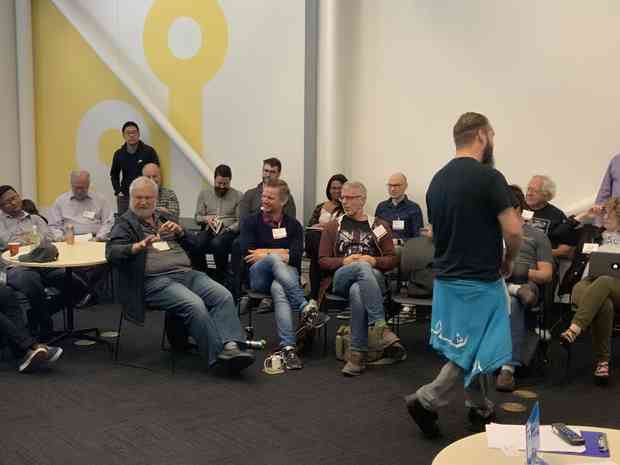
Biggest laugh at #IIW so far: when @justin__richer in his session on “Is #selfsovereignidentity really possible” turned to Dave Crocker and said that we can all blame him for the Internet not having #security built in from the start.

-
At #IIW session on “Is #selfsovereignidentity really possible”, @xmlgrrl Eve Maler offers perhaps the most concise definition of of #privacy I’ve ever heard: “Privacy is context-controlled choice and respect.” Beautiful. And I believe actually possible with #SSI.

-
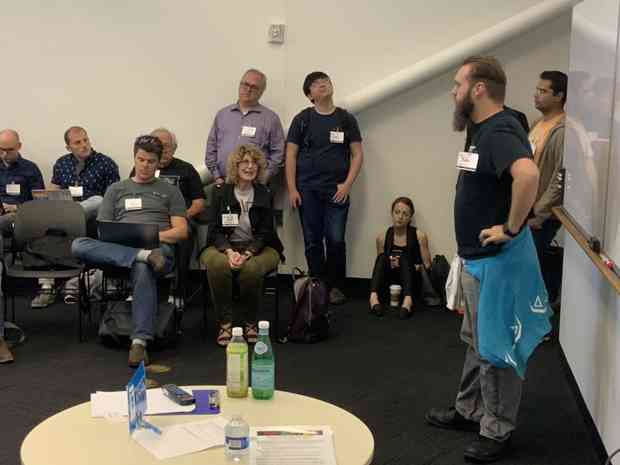
In @justin__richer’s #IIW “DIDn’t” session: Once more with feeling: Privacy is not secrecy; privacy is not encryption; privacy is context, control, choice, and respect.
-
-
San Jose, California • Thu, May 2, 2019 3:57pm
-
San Jose, California • Thu, May 2, 2019 3:48pm
-
San Jose, California • Thu, May 2, 2019 3:43pm
-
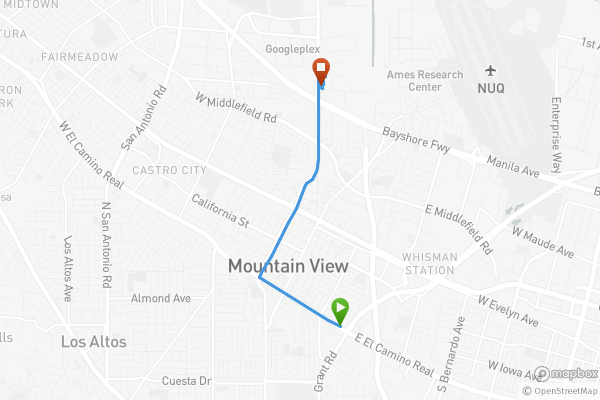
Taxi10.54miDistance34:47DurationStartEnd
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
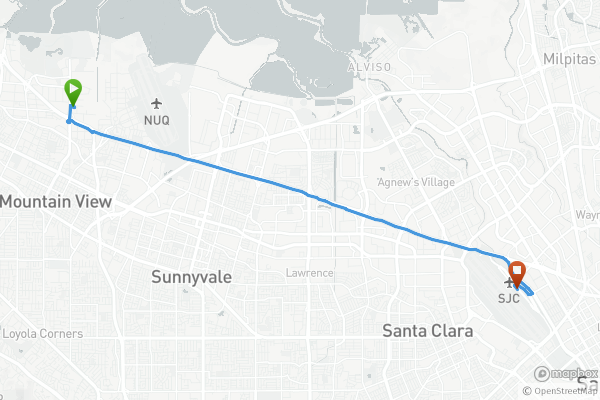
Taxi3.70miDistance102:40DurationStartEnd